GST Summary Comparison in Tally and Excel is one of the most critical processes for businesses, accountants, and tax professionals in India. In the first 100 words itself, it is important to understand that GST compliance is not just about filing returns but also about ensuring that data reported in accounting software like Tally perfectly matches analytical summaries prepared in Excel. Even a small mismatch in taxable value, CGST, SGST, or IGST can result in notices, penalties, or delayed refunds. This detailed article explains how GST summaries are generated in Tally and Excel, how they differ, and how to compare them effectively for error-free compliance.
What Is a GST Summary and Why It Matters
A GST summary is a consolidated snapshot of all GST-related transactions for a specific period. It includes outward supplies, inward supplies, tax liability, input tax credit, and net payable tax.
Businesses rely on GST summaries to:
- File periodic GST returns accurately
- Reconcile books with GST portal data
- Detect errors in tax classification
- Ensure proper utilization of input tax credit
According to industry estimates, over 65% of GST notices issued to small and medium businesses arise due to mismatches between accounting data and GST returns. This highlights why GST summary comparison in Tally and Excel is not optional but essential.
Understanding GST Summary in Tally
Tally generates GST summaries directly from accounting entries. Once GST is enabled and ledgers are correctly configured, Tally automatically classifies transactions into taxable, exempt, zero-rated, and reverse charge categories.
Key Components of GST Summary in Tally
- Total taxable value
- CGST, SGST, and IGST breakup
- Input tax credit summary
- Return-wise summary aligned with GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B
Advantages of Tally GST Summary
- Real-time data from books
- Automatic tax calculation
- Built-in compliance structure
- Lower risk of manual calculation errors
However, Tally summaries depend entirely on correct ledger setup. A single wrong GST rate or ledger classification can distort the entire summary.
Understanding GST Summary in Excel
Excel-based GST summaries are usually prepared by exporting data from Tally or other systems and then restructuring it manually or through formulas. Many accountants prefer Excel because it allows deep customization and flexible analysis.
Key Components of GST Summary in Excel
- Voucher-wise taxable values
- Rate-wise GST calculation
- ITC eligibility analysis
- Month-on-month comparison
Advantages of Excel GST Summary
- High flexibility in reporting
- Custom formats for management review
- Easy reconciliation with portal data
- Advanced analysis using Pivot Tables
The downside is that Excel relies heavily on human accuracy. Studies show that nearly 88% of spreadsheets contain at least one error, which makes reconciliation skills crucial.
GST Summary Comparison in Tally and Excel: Core Differences
The real value emerges when both summaries are compared side by side. This comparison helps identify inconsistencies that may otherwise go unnoticed.
Comparison Table: GST Summary in Tally vs Excel
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Data Source | Tally uses live accounting entries, Excel uses imported or manually structured data |
| Accuracy Control | Tally depends on ledger setup, Excel depends on formulas and data validation |
Why GST Summary Comparison in Tally and Excel Is Essential
1. Detection of Classification Errors
Misclassification of GST rates (5%, 12%, 18%, 28%) is one of the most common issues. Comparing summaries helps detect such mistakes early.
2. Input Tax Credit Reconciliation
ITC mismatches can block working capital. A proper comparison ensures that eligible ITC claimed in returns matches accounting records.
3. Audit and Assessment Readiness
During audits, authorities often ask for reconciled GST data. A well-documented GST summary comparison strengthens audit defense.
4. Reduction in Interest and Penalties
Even a delay caused by mismatch can attract interest at 18% per annum. Regular comparison minimizes this risk.
Step-by-Step Process for GST Summary Comparison in Tally and Excel
Step 1: Generate GST Summary in Tally
Select the reporting period and extract GST summaries including outward supplies, inward supplies, and ITC.
Step 2: Export Data to Excel
Export voucher-level or summary-level data from Tally into Excel format for detailed analysis.
Step 3: Prepare Excel GST Summary
Use formulas or pivot tables to consolidate taxable values and GST amounts rate-wise.
Step 4: Match Key Figures
Compare taxable value, CGST, SGST, IGST, and total tax liability.
Step 5: Identify and Rectify Differences
Check ledgers, vouchers, and GST rates for mismatches and correct them in Tally.
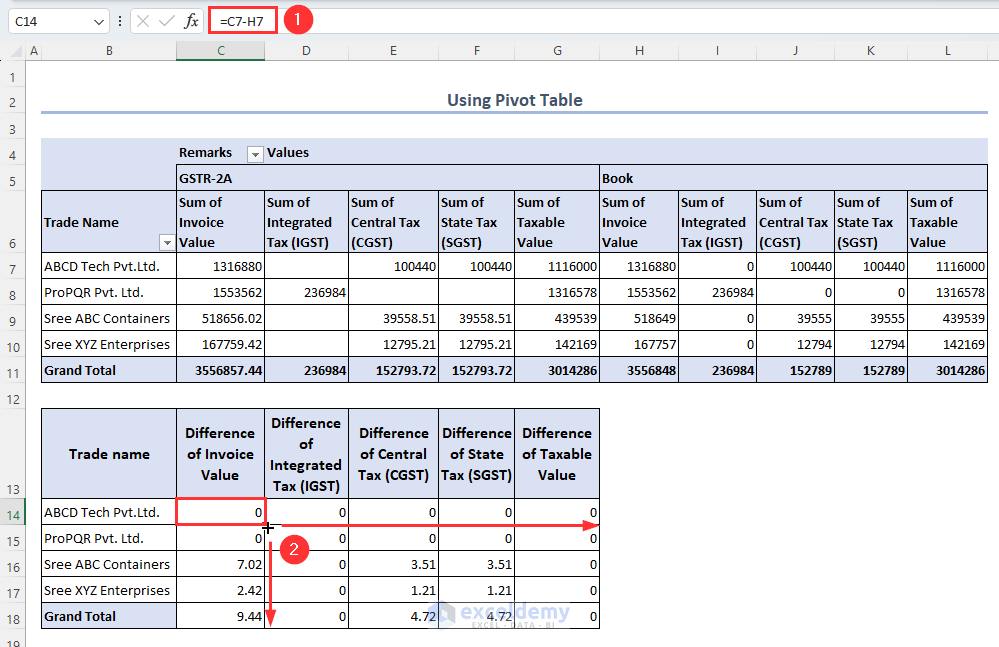
Common Reasons for Differences Between Tally and Excel GST Summaries
- Wrong GST rate selected in ledger
- Incorrect place of supply
- Missing reverse charge entries
- Manual Excel formula errors
- Rounding differences
In practice, rounding differences alone account for nearly 10–12% of minor mismatches, especially in high-volume transactions.
Best Practices for Accurate GST Summary Comparison
- Use standardized Excel templates every month
- Lock GST rates in Tally ledgers
- Perform monthly reconciliation instead of annual
- Maintain documentation for adjustments
- Review summaries before filing returns
Regular monthly reconciliation can reduce year-end workload by up to 40%, according to accounting workflow studies.
GST Summary Comparison in Tally and Excel for Different Returns
GSTR-1 Perspective
Focus on outward supplies, invoice values, and tax breakup.
GSTR-3B Perspective
Focus on summary-level tax liability and ITC utilization.
Aligning both summaries ensures that outward tax declared and tax paid are consistent.
Impact of GST Summary Comparison on Business Decision-Making
Beyond compliance, reconciled GST summaries help businesses:
- Forecast tax outflows
- Optimize pricing strategies
- Improve cash flow planning
- Avoid surprise tax demands
Large businesses report saving 2–3% of annual tax outflow by identifying excess tax payments through proper reconciliation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is GST Summary Comparison in Tally and Excel?
It is the process of matching GST figures generated in Tally with GST summaries prepared in Excel to ensure accuracy and compliance.
2. Why do GST summaries differ between Tally and Excel?
Differences arise due to ledger misclassification, incorrect GST rates, manual Excel errors, or rounding differences.
3. How often should GST summary comparison be done?
Ideally, it should be done monthly before filing GST returns to avoid cumulative errors.
4. Is Excel mandatory for GST reconciliation?
No, but Excel provides flexibility and detailed analysis that complements system-generated summaries.
5. Can GST summary comparison help during audits?
Yes, reconciled summaries provide strong documentary evidence during audits and assessments.
6. What is the biggest risk of not comparing GST summaries?
The biggest risk is incorrect return filing, leading to interest, penalties, and blocked input tax credit.
Conclusion
GST Summary Comparison in Tally and Excel is a foundational practice for accurate GST compliance in India. Tally offers automation and real-time accuracy, while Excel provides analytical depth and flexibility. When both are used together, businesses gain complete control over their GST data. With increasing scrutiny and data-driven compliance, regular and structured comparison is no longer optional but a necessity for sustainable and compliant business operations.
Disclaimer
This article is for educational and informational purposes only. GST laws, rules, and interpretations are subject to change. Readers should verify figures and compliance requirements independently and apply professional judgment before making accounting or tax decisions.
