Automating data cleaning in Excel using Power Query has become a game-changer for accountants, MIS executives, analysts, and business owners who work with large and repetitive datasets. Manual cleaning methods like formulas, filters, and copy-paste are time-consuming and error-prone. Power Query eliminates these issues by allowing you to clean data once and reuse the same logic again and again.
This comprehensive guide explains how to automate data cleaning in Excel using Power Query, why it is superior to traditional methods, and how it can save hours of repetitive work every month. The article is designed for practical, real-world use and is especially relevant for GST data, sales reports, bank statements, payroll files, and MIS dashboards.
What Is Power Query in Excel?
Power Query is a built-in data transformation and automation tool in Excel that allows users to:
- Import data from multiple sources
- Clean, transform, and standardize data
- Apply repeatable steps that refresh automatically
- Eliminate manual data preparation tasks
Power Query works on a step-based transformation model, meaning every action you perform is recorded and can be replayed on new data with a single refresh.
Power Query is part of Excel versions starting from Excel 2016 and Microsoft 365, developed by Microsoft to handle growing data complexity.
Why Automate Data Cleaning Instead of Manual Excel Cleaning?
Manual cleaning becomes inefficient as data volume increases. Power Query solves common Excel problems that formulas alone cannot handle efficiently.
| Manual Data Cleaning | Power Query Automation |
|---|---|
| Needs repeated effort | One-time setup |
| High risk of human error | Rule-based and consistent |
| Slow for large files | Optimized for big data |
| Difficult to audit | Transparent step history |
Fact: Professionals using Power Query report 60–80% reduction in data preparation time, especially when working with recurring reports.
Types of Data Problems Power Query Can Fix Automatically
Power Query is designed specifically to address messy and unstructured data. Below are the most common issues it can automate.
1. Removing Extra Spaces and Non-Printable Characters
Data imported from accounting software or web portals often contains hidden spaces that break formulas. Power Query can clean these instantly.
2. Standardizing Text Case
Customer names, vendor names, and item descriptions often appear in mixed cases. Power Query can convert all text to upper, lower, or proper case consistently.
3. Splitting and Merging Columns
Invoices and bank statements frequently combine multiple values in one column. Power Query can split data using delimiters or positions.
4. Removing Duplicates Automatically
Duplicate entries in ledgers and transaction data are common. Power Query removes duplicates based on defined columns without manual checks.
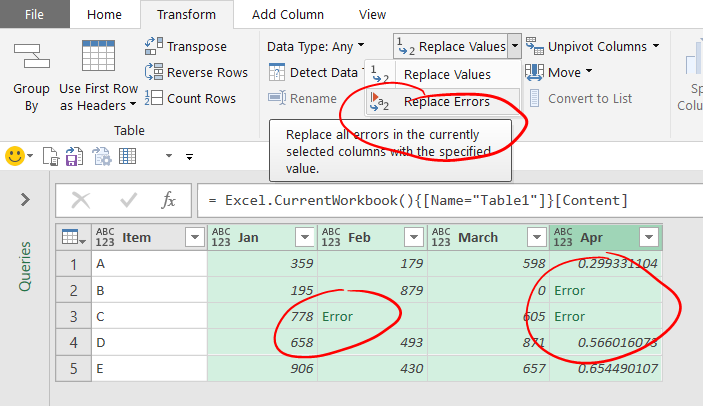
5. Handling Missing or Blank Values
Power Query can replace blanks with zero, text, or previous values using fill logic.
How Power Query Automation Works
Power Query follows a structured transformation process:
- Import raw data
- Apply cleaning and transformation steps
- Load cleaned data into Excel
- Refresh when source data changes
Once created, the same steps apply every time new data is added.
Step-by-Step: Automate Data Cleaning in Excel Using Power Query
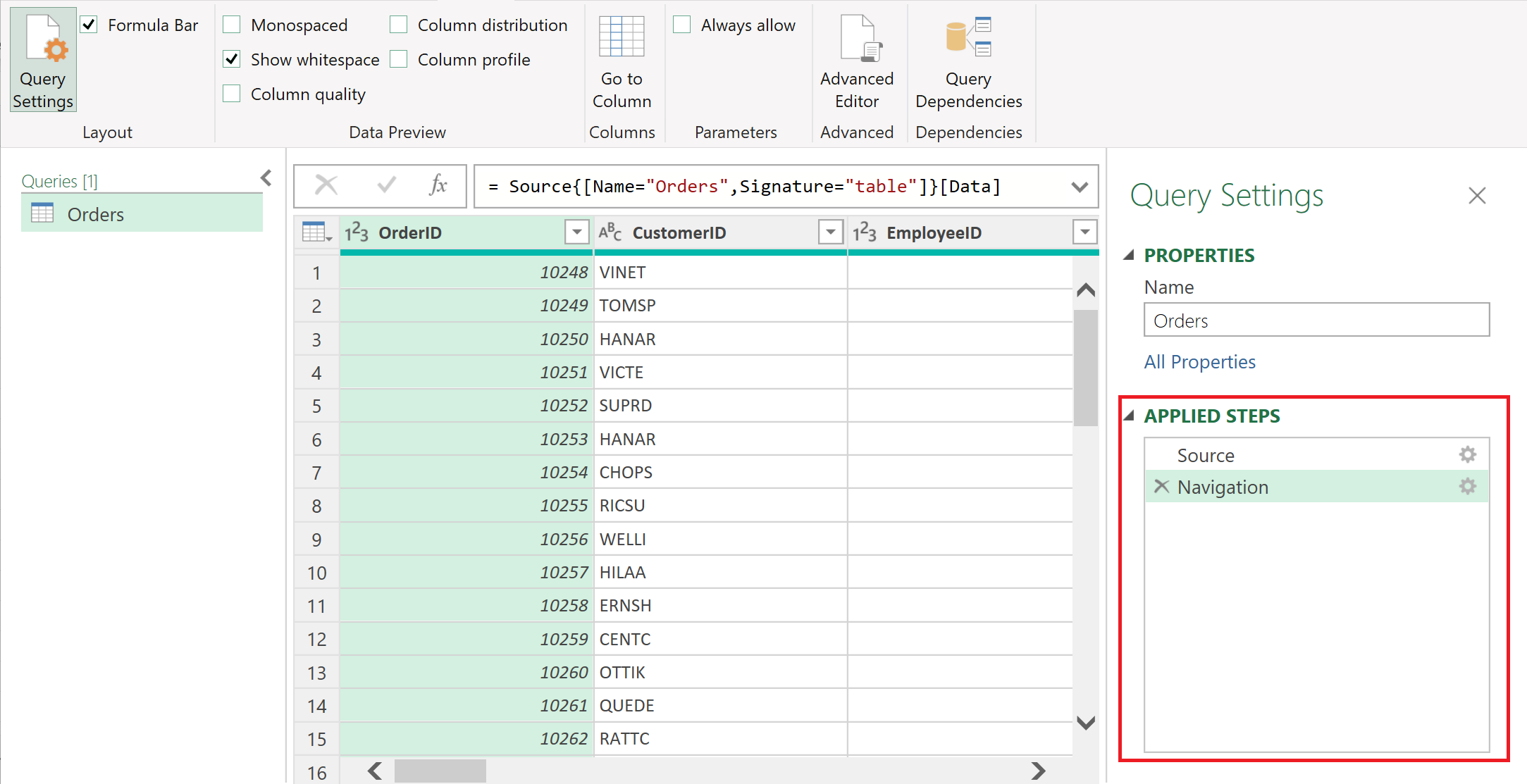
4
Step 1: Load Data into Power Query
Use “Get Data” to import files such as Excel, CSV, text, or folders containing monthly data files.
Step 2: Remove Unnecessary Rows and Columns
Delete empty rows, summary rows, or unwanted columns to reduce file size and processing time.
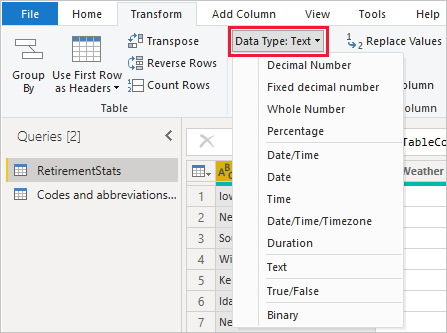
Step 3: Clean and Transform Data
Apply transformations such as:
- Trim and clean text
- Change data types (text, number, date)
- Replace values
- Split columns
Each action is recorded as a step.
Step 4: Standardize Formats
Ensure dates, currency, and numeric fields follow a uniform structure to avoid reporting errors.
Step 5: Load Clean Data
Load the final cleaned dataset into Excel tables or directly into reports.
Power Query vs Excel Formulas for Data Cleaning
| Feature | Excel Formulas | Power Query |
|—|—|
| Learning Curve | Low | Moderate |
| Automation Level | Limited | High |
| Large Data Handling | Slow | Efficient |
| Repeatability | Manual | One-click refresh |
Power Query is not a replacement for formulas, but a complementary tool focused on data preparation rather than analysis.
Real-World Use Cases of Power Query Automation
GST Return Preparation
- Clean sales registers
- Standardize invoice formats
- Remove invalid GSTIN entries
Bank Reconciliation
- Import monthly bank statements
- Normalize debit/credit columns
- Match transactions automatically
Payroll Processing
- Merge attendance data
- Standardize employee IDs
- Prepare salary input sheets
MIS Reporting
- Combine multiple monthly files
- Create clean master datasets
- Feed dashboards without manual edits
Best Practices for Power Query Automation
- Always set correct data types early
- Keep transformation steps minimal and logical
- Name queries clearly for audit clarity
- Avoid unnecessary calculated columns
- Use folder-based imports for recurring data
Figure Insight: A well-designed Power Query workflow can process 100,000+ rows in seconds, depending on system configuration.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Using Power Query
- Ignoring data type mismatches
- Loading unnecessary columns
- Creating separate queries for similar tasks
- Overusing custom columns when built-in transformations exist
Avoiding these mistakes ensures stable and scalable automation.
Is Power Query Suitable for Non-Technical Users?
Yes. Power Query is no-code or low-code, making it accessible to accountants and MIS users with basic Excel knowledge. Most transformations are done through menus, not formulas.
Future Scope of Power Query in Excel Automation
Power Query is increasingly becoming the foundation for:
- Automated MIS systems
- Business intelligence reporting
- Data pipelines feeding dashboards
As data volumes grow, Power Query skills are becoming essential for finance and accounting professionals.
Conclusion: Why You Should Automate Data Cleaning in Excel Using Power Query
Automating data cleaning in Excel using Power Query is no longer optional for professionals dealing with repetitive data tasks. It ensures accuracy, consistency, scalability, and massive time savings. Once implemented, it transforms Excel from a manual tool into an automated data engine.
For accountants, analysts, and business users, Power Query represents a long-term productivity investment that pays back every single month.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the main advantage of using Power Query for data cleaning?
Power Query allows one-time cleaning rules that refresh automatically, saving time and reducing errors.
2. Can Power Query handle large datasets?
Yes, it efficiently handles tens of thousands of rows better than traditional Excel formulas.
3. Is Power Query available in all Excel versions?
Power Query is built-in from Excel 2016 onward and in Microsoft 365 versions.
4. Do Power Query changes affect original data?
No, Power Query works on a copy of the data and never modifies the source file.
5. Is coding required to use Power Query?
No coding is required for most tasks; transformations are menu-driven.
6. Can Power Query be refreshed automatically?
Yes, queries can be refreshed manually or set to refresh when files are updated.
7. Is Power Query useful for GST and accounting data?
Yes, it is highly effective for GST returns, sales registers, and reconciliation work.
Disclaimer
This article is intended for educational and informational purposes only. Features, performance, and availability of Excel tools may vary depending on version and system configuration. Readers should evaluate suitability based on their specific business and operational requirements.
