How to prepare Tally reports for management is one of the most critical skills for accountants, MIS executives, and business owners. Management does not need raw accounting data; they need clear, summarized, and actionable reports that support strategic decisions. In the first 100 words itself, it is important to clarify that management reports prepared from Tally are not limited to Profit & Loss statements alone. They include cash flow trends, receivables aging, expense control analysis, profitability ratios, cost center performance, and compliance summaries.
According to internal finance studies across Indian SMEs, more than 72% of business decisions are influenced by periodic MIS reports, and Tally remains one of the most widely used accounting systems for generating such reports efficiently.
What Are Management Reports in Tally?
Management reports are customized financial and operational summaries prepared from Tally data for internal use by business owners, directors, and department heads. Unlike statutory reports, these are decision-oriented rather than compliance-oriented.
Management reports generally answer questions such as:
- Is the business profitable this month compared to last month?
- Where is cash getting blocked?
- Which expenses are rising abnormally?
- Which customers or products generate the highest margins?
Key Characteristics of Management Reports
- Periodic (daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly)
- Comparative in nature
- Focused on trends rather than entries
- Simple language with figures, not accounting jargon
Why Management Needs Reports from Tally
Tally records thousands of transactions, but management cannot analyze raw vouchers. Structured reports convert data into insights.
Key reasons why management reports are essential:
- Improve financial control
- Enable faster decision-making
- Identify cost leakages
- Track business growth in numbers
- Support budgeting and forecasting
A mid-sized organization typically reviews 8–12 core MIS reports every month, most of which can be generated directly from Tally with proper configuration.
Core Tally Reports Used for Management Decision-Making
4
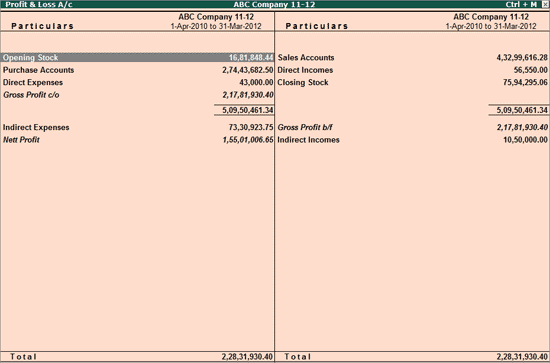
1. Profit and Loss Report (Management View)
The Profit & Loss account is the backbone of management reporting. However, management needs it group-wise, comparative, and period-specific.
Best practices:
- Compare current month vs previous month
- Compare actual vs budgeted figures
- Analyze operating vs non-operating income
Fact: Businesses that review P&L monthly reduce unnecessary expenses by 12–18% annually.
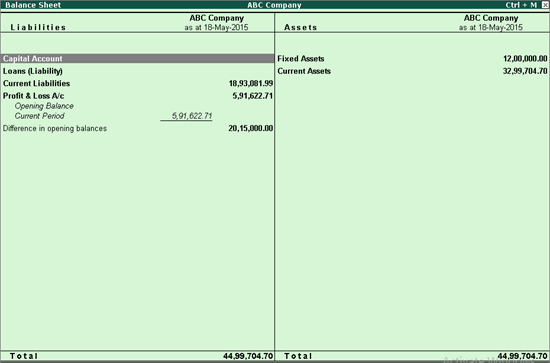
2. Balance Sheet Summary for Management
Management does not require ledger-level details. Instead, they focus on:
- Capital structure
- Loan position
- Asset utilization
- Working capital strength
Use group-level summaries instead of detailed schedules while presenting.
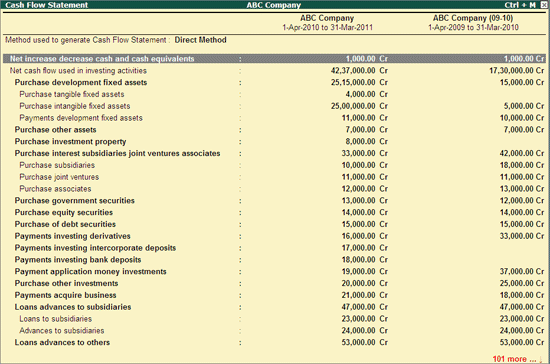
3. Cash Flow and Fund Flow Reports
Cash flow reports help management understand actual liquidity, not just profits.
Key insights derived:
- Operating cash surplus or deficit
- Dependency on borrowings
- Timing mismatch between income and expenses
Nearly 65% of profitable businesses face cash shortages due to poor cash flow tracking.
4. Receivables and Payables Aging Analysis
Aging analysis highlights how long money is blocked.
| Aging Category | Management Insight |
|---|---|
| 0–30 Days | Healthy collection cycle |
| Above 90 Days | High risk of bad debts |
This report helps management tighten credit policies and improve cash inflow.
Preparing Cost Center and Profit Center Reports in Tally
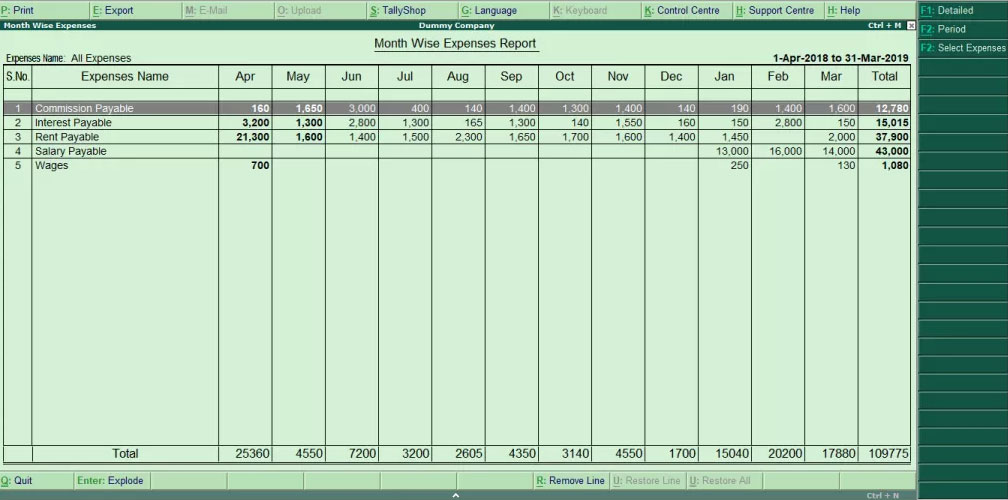

Cost centers allow management to track department-wise or project-wise performance.
Examples of Cost Centers
- Sales Department
- Marketing Campaigns
- Branch Offices
- Projects or Contracts
Management Advantage:
Companies using cost center reports achieve up to 20% better cost control compared to those without internal segmentation.
Budget vs Actual Reports for Management Control
Budgeting in Tally enables proactive management.
| Report Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Budget vs Actual | Expense control and planning |
| Variance Report | Identify deviations early |
A variance beyond ±5% generally requires management attention.
Sales and Purchase Analysis Reports
Sales reports are essential for growth tracking.
Sales Analysis Parameters
- Monthly sales trend
- Product-wise contribution
- Region-wise performance
Purchase analysis helps in:
- Vendor dependency analysis
- Cost optimization
- Inventory planning
Fact: Inventory and procurement decisions influence nearly 40% of total operating costs in trading businesses.
Ratio Analysis Reports for Management
Management often prefers ratios over absolute figures.
Important Ratios to Present
- Gross Profit Ratio
- Net Profit Ratio
- Current Ratio
- Debtors Turnover Ratio
Ratios simplify complex financial data into quick performance indicators.
Customizing Tally Reports for Management Presentation
Raw reports should be customized before sharing.
Customization Techniques
- Set period filters
- Enable comparative columns
- Hide zero-value groups
- Export to Excel for dashboards
Most management teams prefer one-page summaries rather than lengthy statements.
Monthly MIS Structure Using Tally Reports
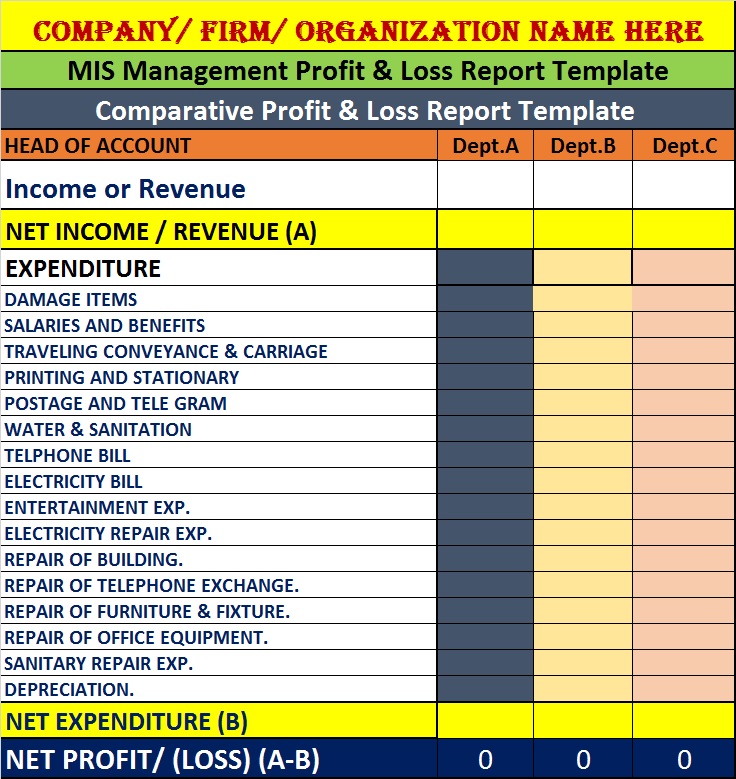

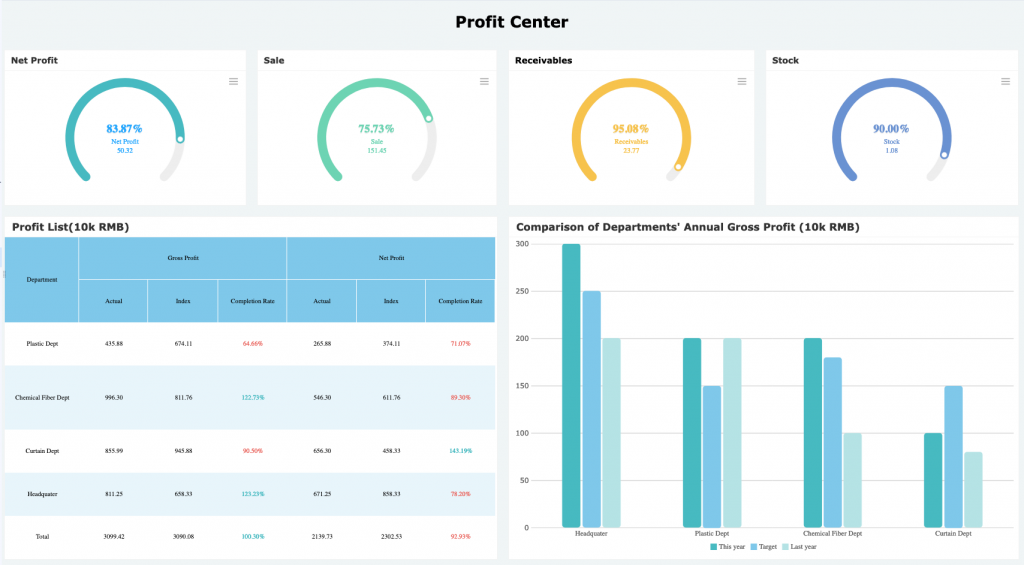
A standard monthly MIS prepared from Tally includes:
- Profit & Loss Summary
- Balance Sheet Snapshot
- Cash Flow Statement
- Receivables & Payables Aging
- Expense Variance Report
- Key Ratios Summary
Such MIS packs typically range between 6–10 pages and are reviewed within 15–20 minutes by top management.
Common Mistakes While Preparing Tally Reports for Management
- Sharing ledger-level details instead of summaries
- Ignoring comparative analysis
- Not reconciling data before reporting
- Mixing statutory and management formats
- Overloading reports with accounting terms
Avoiding these mistakes improves report acceptance and credibility.
Best Practices for High-Impact Management Reporting
- Maintain accurate masters and groups
- Close books monthly before reporting
- Use consistent formats every period
- Highlight key numbers and deviations
- Add short explanatory notes
Well-prepared reports increase trust in the finance team and reduce repetitive management queries.
FAQ: How to Prepare Tally Reports for Management
1. What is the most important Tally report for management?
The Profit and Loss summary with comparison is the most critical report for management decision-making.
2. How frequently should management reports be prepared?
Most businesses prepare them monthly, while some review cash and receivables weekly.
3. Can Tally reports be customized for management use?
Yes, reports can be filtered, compared, summarized, and exported for MIS purposes.
4. Do management reports differ from statutory reports?
Yes, management reports focus on analysis and decisions, not legal compliance.
5. What level of detail is ideal for management?
Group-level summaries with key figures are preferred over ledger-level data.
6. Are cost center reports necessary for small businesses?
Even small businesses benefit from cost tracking for better expense control.
Conclusion
Understanding how to prepare Tally reports for management transforms accounting data into powerful business intelligence. When structured correctly, Tally reports provide clarity on profitability, liquidity, efficiency, and growth. Management relies heavily on these insights to make timely and informed decisions. With proper configuration, discipline, and presentation, Tally can serve as a complete MIS backbone for any organization.
Disclaimer
This article is intended for educational and informational purposes only. Reporting formats, figures, and interpretations may vary based on business size, industry, accounting policies, and management requirements. Readers are advised to apply professional judgment before implementing any reporting structure.
