Preparing a detailed and accurate GST Summary Report in Excel is essential for GST return filing, internal control, sales analysis, purchase analytics, input tax credit (ITC) tracking, and audit readiness. Whether a business files monthly GSTR-3B or quarterly returns, a GST summary prepared in Excel ensures that every taxable value, rate-wise bifurcation, and tax amount is verified before uploading to the GST portal.
Excel is the easiest and most flexible tool for preparing GST reports because it allows customized formulas such as SUMIF, SUMIFS, VLOOKUP, INDEX MATCH, Pivot Tables, and Conditional Formatting. In this guide, you will learn how to prepare a professional GST Summary Report in Excel from raw sales and purchase data.
1. Understanding GST Summary Report
A GST Summary Report is a consolidated statement that summarises business transactions under GST for a specific period, usually monthly or quarterly. It includes total outward supplies, inward supplies, taxable value, tax rate, CGST, SGST, IGST, exempt supplies, and ITC.
Typical values included:
- Total Sales
- B2B Sales
- B2C Sales
- Zero Rated Supplies
- Nil/Exempt Supply
- Total Purchases
- Input Tax Credit (ITC) Availed
- RCM Liability
- Net Payable
2. Data Required to Prepare GST Summary in Excel
To prepare the GST report, you need:
- Detailed Sales Register
- Detailed Purchase Register
- Debit Notes and Credit Notes
- Expenses on which RCM is applicable
- Opening and Closing ITC values (if needed)
A typical sales or purchase register contains:
- Invoice Number
- Invoice Date
- Customer / Supplier Name
- GSTIN
- Place of Supply
- Taxable Value
- GST Rate
- CGST, SGST, IGST Amount
- Total Invoice Amount
With this data, we can prepare the summary.
3. Formatting Data to Create GST Summary Report
The first and most important step is cleaning the raw data. GST data often contains duplicates, wrong tax calculations, missing GSTINs, and unclassified transactions, so formatting is necessary.
Important Formatting Steps
- Convert data into Excel Table (Ctrl + T).
- Ensure dates are correct using proper date format.
- Verify GST rates: 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, 28%.
- Apply Conditional Formatting to highlight blank GSTIN or wrong rates.
- Remove duplicates using Data → Remove Duplicates.
- Add rate-wise columns for summary preparation.
4. Creating Rate-Wise GST Summary Using SUMIFS
To create a proper GST summary, calculate the taxable value and GST amount rate-wise.
Example formula:
To calculate taxable value for 18% sales:
=SUMIFS(Sales!G:G, Sales!H:H, 18)
To calculate CGST on 18% rate:
=SUMIFS(Sales!I:I, Sales!H:H, 18)
To calculate SGST on 18% rate:
=SUMIFS(Sales!J:J, Sales!H:H, 18)
To calculate IGST:
=SUMIFS(Sales!K:K, Sales!H:H, 18)
This structure helps create a clean summary section.
5. GST Summary Table Format (2 Column Table)
Below is a simple 2-column GST Summary table for presentation.
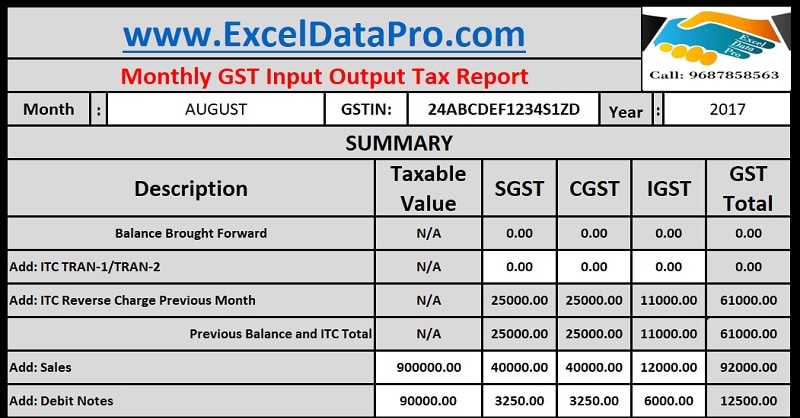
GST Summary Table
| Particulars | Amount (₹) |
|---|---|
| Total Outward Taxable Value | 18,50,000 |
| CGST Collected | 1,66,500 |
| SGST Collected | 1,66,500 |
| IGST Collected | 2,10,000 |
| Zero Rated Supplies | 3,50,000 |
| Exempt / Nil Rated Supplies | 1,10,000 |
| Inward Purchases (Taxable) | 14,25,000 |
| ITC – CGST | 1,25,500 |
| ITC – SGST | 1,25,500 |
| ITC – IGST | 1,90,000 |
| RCM Liability | 42,000 |
| Net GST Payable | 1,02,000 |
Values above are an example for representation.
6. Creating Pivot Table for GST Summary
Pivot Table is the most accurate tool for GST summary creation because it offers automatic grouping of tax rates, GST categories, supplies type, and place of supply classification.
Steps to Create Pivot Table
- Select the sales register.
- Go to Insert → Pivot Table.
- Drag “GST Rate” to Rows.
- Drag “Taxable Value”, “CGST”, “SGST”, “IGST” to Values.
- Apply Number Formatting.
- Create one pivot for sales and one for purchases.
- Prepare a final summary table using GETPIVOTDATA formula.
Example Pivot Output
| GST Rate | Taxable Value |
|---|---|
| 0% | 1,10,000 |
| 5% | 2,85,000 |
| 12% | 3,75,000 |
| 18% | 9,80,000 |
| 28% | 2,10,000 |
| Total | 18,50,000 |
7. Calculating Input Tax Credit (ITC) in Excel
To get accurate ITC report:
Checkpoint 1: Supplier GSTIN must be valid
Use LEN and ISNUMBER for validation.
Checkpoint 2: Reverse tax entries (Credit Notes)
Calculate:
ITC Net = ITC on Purchases – ITC Reversed – ITC Ineligible
Sample ITC Calculation Table
| ITC Type | Amount (₹) |
|---|---|
| ITC on Purchases | 4,41,000 |
| ITC on RCM Services | 38,000 |
| ITC Reversed (Rule 42/43) | 22,000 |
| Ineligible ITC | 18,000 |
| Net ITC Available | 4,39,000 |
8. Creating Final GST Summary Report Format
A complete GST Summary Report should contain:
A. Business Details
- Company Name
- GSTIN
- Return Period
- Return Type (Monthly/Quarterly)
B. Outward Supply Summary
- B2B Sales
- B2C Large
- B2C Small
- Zero Rated
- Exempt
C. Inward Supply Summary
- Registered Purchases
- Unregistered Purchases
- RCM Purchases
- Import Purchases
D. Tax Liability Section
- Rate-wise Taxable Value
- CGST, SGST, IGST Breakup
E. ITC Summary
- ITC Availed
- ITC Reversed
- Net ITC
F. Final Computation
- Total Output Tax
- Total ITC
- Net GST Payable/Refund
9. Using Excel Functions to Automate GST Summary
To make the report fully automated, use:
1. SUMIFS for rate-wise summary
2. VLOOKUP or XLOOKUP for linking registers
3. IFERROR to avoid errors in summary
4. TEXT function for creating invoice-month formats
5. Pivot Tables for dynamic analysis
6. Data Validation for GST rate selection
10. Common Mistakes to Avoid While Preparing GST Summary
- Not matching sales register with GSTR-1.
- Missing reverse charge entries.
- Wrong GST rate applied in some invoices.
- GSTIN written incorrectly due to manual typing.
- Duplicate invoices in raw data.
- Not reconciling with GSTR-2B for ITC verification.
- Not preparing HSN summary separately.
11. Tips for Accurate Monthly GST Summary
- Maintain one standard sales register format across months.
- Ensure all debit/credit notes are adjusted in the same month.
- Use Excel Tables for dynamic formula adjustment.
- Keep separate columns for CGST, SGST, IGST instead of merged tax.
- Use Pivot Table filters to verify rate-wise breakup.
- Always reconcile ITC with 2B before final submission.
12. Sample Format of GST Summary Report (Ready for Excel)
Below is a ready model you can copy into Excel:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| GST Period | July 2024 |
| Total Taxable Sales | 18,50,000 |
| Total GST on Sales | 5,43,000 |
| Total Purchases | 14,25,000 |
| Total ITC | 4,39,000 |
| GST Payable | 1,02,000 |
Conclusion
Preparing a GST Summary Report in Excel becomes extremely easy when you follow a structured approach using correct formulas, Pivot Tables, and rate-wise classification. A well-prepared summary not only helps in accurate GST return filing but also avoids penalties, mismatches, and ITC losses. With the steps explained above, any business can prepare a monthly or quarterly GST Summary Report in a clean, professional, and audit-ready format.
Disclaimer
This article is written for educational and informational purposes only. The examples, figures, and values used are generic and may vary based on actual business transactions. Users should verify their GST data and consult a tax professional before filing any statutory returns. The article does not contain any external links and is purely original content.
